Call Us Today!
(425) 999-8159
New Patients
(425) 264-7102
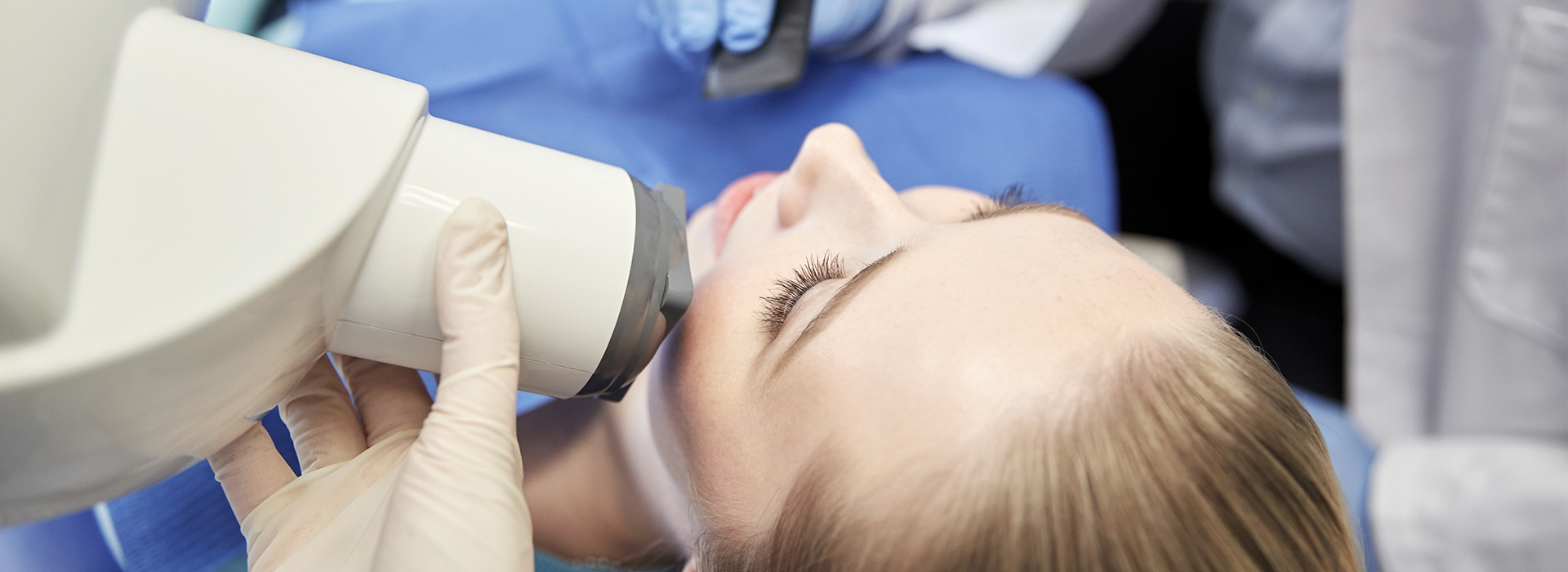
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with electronic sensors and computer technology to capture detailed images of teeth, bone, and supporting structures. Unlike conventional X-ray film, these images are created as digital files that can be viewed immediately on a monitor, adjusted for clarity, and stored securely within a patient’s record. This streamlined process improves diagnostic accuracy and makes routine imaging more efficient for both patients and clinicians.
At the office of 360 Dental of Mill Creek, we use digital imaging as an integral part of comprehensive dental care. The technology helps our team detect cavities, evaluate bone health, monitor root development, and plan complex restorative or implant treatments with greater precision. For patients, that means examinations can be more informative and conversations about treatment options are grounded in clear visual evidence.
Digital radiography preserves diagnostic detail while eliminating many steps associated with film development. The result is faster appointments, clearer communication, and a reduced likelihood of repeat images due to exposure or processing errors. Patients benefit from a modern workflow that supports better outcomes and a more comfortable experience.
Because digital files are easily archived and retrieved, they also support continuity of care—images taken at one visit can be compared with later studies to monitor changes over time. This capability is particularly valuable for long-term periodontal monitoring, evaluating the progression of restorative work, or tracking the healing process after surgery.
One of the most meaningful advantages of digital radiography is the reduction in radiation exposure compared with traditional film X-rays. Digital sensors are more sensitive to X-ray beams, which means quality images can be produced with significantly lower doses. While all dental imaging follows strict safety guidelines, minimizing exposure whenever possible is a practical improvement for routine care.
Another immediate patient benefit is speed. Digital images appear on-screen within seconds of capture, so clinicians can review findings with the patient during the same visit. This immediacy reduces wait times, helps patients understand their oral health more quickly, and supports shared decision-making during the appointment.
Because images can be enlarged and enhanced on-screen, small details that might be missed on film become more visible. This capability enables early detection of issues like incipient decay, hairline fractures, or subtle bone changes—allowing for less invasive interventions and more predictable treatment planning.
Digital radiography relies on a compact sensor placed in the mouth to capture X-ray photons and convert them into an electronic image. These sensors connect to a computer system that processes the raw data and produces an image that can be manipulated—adjusting contrast, brightness, and sharpness—to highlight areas of interest. The software tools that accompany digital radiography are as important as the sensors themselves, enabling clinicians to fine-tune images for diagnostic clarity.
Once acquired, images are saved directly into the patient’s electronic record, eliminating darkrooms, chemical developers, and physical film storage. This integration makes it easier to track a patient’s history, compare successive images side-by-side, and include visuals in treatment notes. Files can also be exported in standard formats when specialist consultations or referrals are necessary.
Advanced processing tools include measurement features and annotation capabilities that support precise treatment planning. For example, clinicians can measure bone height for implant planning or mark areas of concern before discussing treatment with the patient. These tools turn images into actionable information rather than just pictures.
Some digital radiography systems also integrate with three-dimensional imaging modalities, allowing for a layered approach to diagnosis that combines 2D and 3D perspectives when clinically indicated. This interoperability enhances diagnostic flexibility without replacing the simpler, lower-dose exams used for routine care.
Digital images improve clinical decision-making by providing consistent, high-resolution views that are easy to compare over time. This consistency supports early detection and more accurate monitoring of conditions such as periodontal disease, recurrent decay beneath restorations, and root or bone pathology. The ability to enhance and magnify images aids clinicians in identifying details that inform more conservative and targeted treatment strategies.
Digital radiography also facilitates collaboration among dental specialists and laboratories. Because files can be shared instantly and securely, clinicians can consult with endodontists, oral surgeons, or prosthodontists and include detailed visuals within referral communications. This collaborative potential shortens the time to coordinated care and helps ensure all members of a treatment team are working from the same information.
For restorative and surgical planning, precise imaging contributes to better outcomes. When clinicians can accurately assess anatomy and existing work—such as previous crowns or root canal treatments—they can design interventions that preserve healthy tissue and align with a patient’s functional needs and aesthetic goals. Digital imagery supports that level of planning without adding undue complexity to routine visits.
Digital radiography minimizes environmental impact by eliminating film, chemical developers, and physical storage needs. Removing chemical processing from the imaging workflow reduces hazardous waste and the need for specialized disposal, making digital imaging a more sustainable choice for dental practices committed to reducing their ecological footprint.
Digital records also require careful attention to privacy and security. Images stored in electronic health records are protected under standard healthcare privacy regulations and practice-level security protocols. These measures include encrypted storage, restricted access, and secure transfer methods when images must be shared with outside providers. Patients can be assured that their imaging data is managed with the same confidentiality as the rest of their dental record.
Radiation safety remains a priority: even though digital sensors reduce exposure, clinicians continue to follow best practices—such as using lead aprons when appropriate, selecting the smallest area of exposure needed, and applying age- and condition-appropriate imaging protocols. These measures ensure that imaging is used judiciously and only when it adds value to diagnosis or treatment planning.
Finally, the practical benefits of digital imaging—faster results, clearer diagnostic information, and easier collaboration—translate into a smoother patient experience. Patients typically appreciate seeing images that explain findings visually, which enhances understanding and participation in their own care.
In summary, digital radiography brings faster, safer, and more precise imaging to routine dental care. The technology enhances diagnostic accuracy, supports efficient treatment planning, and aligns with modern standards for safety and environmental responsibility. To learn more about how we use digital imaging in our office and what it means for your care, please contact us for more information.
Digital radiography uses electronic sensors and computer processing to capture images of teeth, bone and surrounding structures instead of photographic film. Images are produced as digital files that appear on a monitor within seconds, and clinicians can adjust contrast, brightness and magnification to reveal diagnostic detail. This immediate feedback reduces the need for retakes caused by exposure or processing errors and streamlines the clinical workflow.
Unlike film, digital files are easily archived, retrieved and compared over time, which supports continuity of care and long-term monitoring. Eliminating chemical developers and darkroom processes also reduces environmental waste and physical storage needs. The end result is faster appointments, clearer communication and more consistent imaging for diagnosis and treatment planning.
At 360 Dental of Mill Creek, digital radiography is an integral part of comprehensive examinations, treatment planning and follow-up care. The team uses high-resolution images to detect cavities, evaluate bone levels, assess root structure and plan restorative and implant procedures with greater precision. Clinicians review images with patients during the visit so findings are visible, understandable and can guide shared decisions about next steps.
Digital files are stored in the patient record to enable direct comparisons across visits and to support coordinated care when specialists are consulted. Measurement and annotation tools help the team document concerns and plan interventions more accurately, while secure digital transfer ensures relevant images can be shared efficiently when referrals are needed. This combination of technology and clinical workflow enhances diagnostic clarity and patient communication.
Patients benefit from substantially faster imaging and immediate review of results, which reduces time spent waiting for film processing and allows clinicians to explain findings during the same appointment. Digital sensors are more sensitive to X-rays than traditional film, so high-quality diagnostic images can be obtained with lower radiation doses. Enhanced images can be enlarged and adjusted to reveal subtle issues that might be missed on film, supporting earlier intervention when appropriate.
Because images are less likely to require retakes, patients experience fewer repeat exposures and a smoother clinical visit overall. The ease of archiving and comparing digital studies supports long-term monitoring of periodontal health, restorative work and healing after procedures. These operational advantages translate into clearer communication, more informed patients and more predictable treatment planning.
Digital radiography typically requires lower radiation doses than conventional film because modern sensors are more efficient at capturing X-ray photons. Clinicians follow established safety principles such as limiting the exposure area, using appropriate shielding and applying age- and condition-specific imaging protocols to ensure images are taken only when clinically necessary. These measures keep exposure as low as reasonably achievable while still providing diagnostic-quality images.
Dental practices also adhere to regulatory guidance and equipment maintenance standards to ensure consistent performance and safe operation. Proper sensor positioning and operator training reduce the likelihood of retakes, further minimizing cumulative exposure. Patients with specific medical concerns should discuss imaging history and safety considerations with their clinician to establish the best approach for their care.
Digital sensors placed intraorally convert X-ray photons into electronic signals that are processed by dedicated software to create a diagnostic image. The accompanying software provides tools for adjusting contrast, measuring distances, annotating areas of interest and comparing images side-by-side, which helps clinicians identify small changes and quantify clinical findings. These capabilities transform raw data into actionable information for diagnosis, monitoring and treatment planning.
Advanced processing can also enhance visualization of fine details such as hairline fractures, recurrent decay beneath restorations or subtle bone changes. Integration with the patient record means images are immediately available for review and for secure sharing with specialists when consultations are required. Together, sensors and software increase diagnostic confidence and support more targeted, conservative treatment strategies.
Digital radiographs provide precise views of bone height, tooth roots and existing restorative work, which are essential for preoperative assessment and treatment planning. Measurement tools allow clinicians to estimate available bone, identify anatomic landmarks and evaluate the relationship between adjacent teeth and proposed implant sites. When combined with other diagnostic records, digital images inform surgical approaches and the selection of appropriate restorative materials.
For restorative cases, clinicians can use annotated images to communicate margins, evaluate previous endodontic work and anticipate potential complications before treatment begins. Digital files can be exported to dental laboratories and specialists to ensure everyone involved in complex cases is working from the same visual information. This level of preparation contributes to more accurate outcomes and coordinated care across the treatment team.
Digital radiographs are saved directly into the patient’s electronic record and protected by the practice’s security protocols and standard healthcare privacy regulations. Storage systems typically use encrypted databases and restricted access controls so only authorized team members can view or modify imaging files. When images must be transferred to another provider, secure export and transmission methods are used to preserve confidentiality.
Retention and access policies are managed according to legal and clinical guidelines, and patients may be informed about how long records are kept and how they can request copies. Practice-level safeguards, regular system updates and staff training help maintain the integrity and privacy of imaging data. These combined measures ensure that radiographic records are handled with the same care as other protected health information.
The frequency of digital radiographs is not the same for every patient and is determined by clinical need, oral health status, risk factors and treatment plans. Routine imaging intervals may differ for children, adults with active disease and patients undergoing complex restorative or surgical care. Clinicians assess each patient’s history, current exam findings and any symptoms before recommending the type and timing of imaging.
Guidelines emphasize taking images only when they will influence diagnosis or treatment, so the imaging schedule is individualized to minimize unnecessary exposure. Factors such as new or worsening symptoms, changes in periodontal health, restorative follow-up or preparation for surgery can prompt more frequent imaging. Patients should discuss their specific imaging plan with their clinician to understand the rationale for recommended intervals.
During a digital radiography appointment, a small sensor may be placed inside the mouth while the clinician positions an X-ray source outside the mouth to capture the image. Most patients experience only minimal discomfort from sensor placement, and images appear on the monitor within seconds for immediate review. Protective measures such as lead aprons are used when appropriate, and the procedure is quick, typically adding only a few minutes to a dental visit.
After images are acquired, the clinician will review them with the patient, pointing out any areas of concern and explaining how the images inform diagnosis and treatment. Enhanced views and annotations help patients understand findings and the proposed plan of care. If additional or specialized imaging is needed, the clinician will explain the reasons and next steps clearly and factually.
Yes, patients can request copies of their digital radiographs for personal records, second opinions or referrals to specialists, and the practice can provide images in standard formats such as PDF or DICOM when clinically appropriate. Copies are typically prepared for secure transfer or for patient pickup according to the practice’s record-release procedures. Requesting images allows you and any consulting providers to review the same diagnostic information used in care decisions.
When requesting radiographs, it is helpful to specify the date range or the particular images needed so the team can locate and export the correct files efficiently. The practice will coordinate secure transmission methods to protect privacy when sending files outside the office. Patients with questions about the process or required documentation should contact the office for guidance on next steps.
